Graphical Models
13 Jul 2017 | probabilistic-models machine-learningGraphical models are a method of representing uncertatainty and reasoning. To do this generate a graph, and set probabilities for each node in the graph.
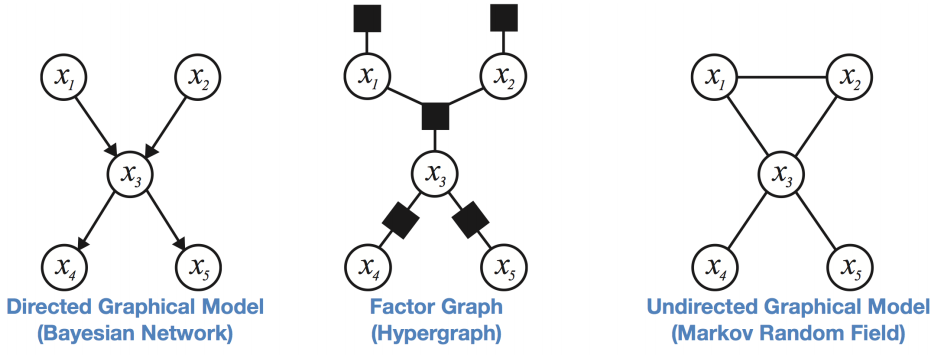
In all cases, nodes are random variables and the graph species a coarse structure of a joint distribution. These graphs have properties of conditional independence from the nodes above their parents.
Markov Chains
Conditioned on the present, the past and future are independent.
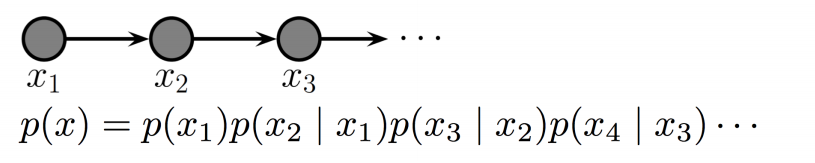
It’s important to note that graph seperation implies conditional independence.
Naive-Bayes
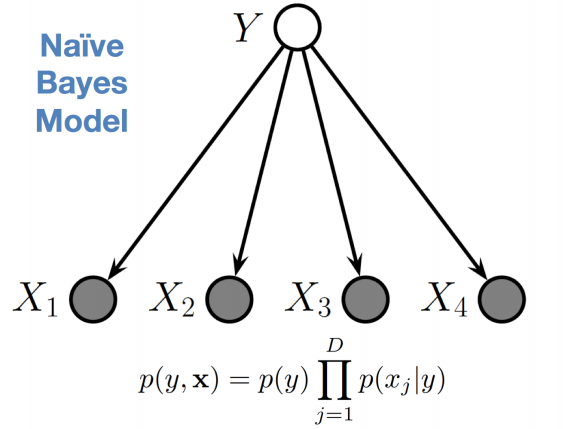
inference takes in a model with known paramaters and estimates the hidden variables
learning takes in multiple data instances and estimates the paramaters for a probabilistic model.
Sum-Product Belief Propogation
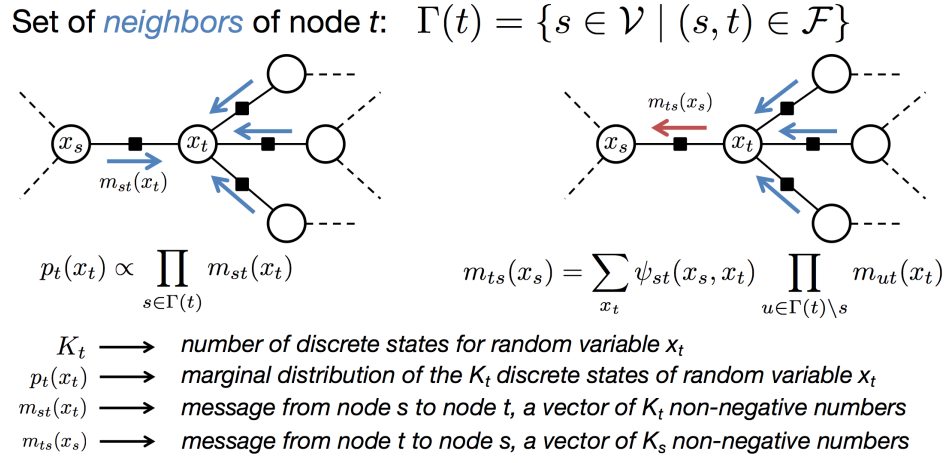
A node may only send a message to a neighbor when it has recieved incoming messages from all of its other neighbors. These messages can either be discrete or continuous (belief propogation)
This can be used to detect the relative postion between features.
